C++ らしく、malloc の代わりに new が使われていることにも注意。
s1 はオブジェクト o に対応する。s が o.p に変更されていること以外は「文字列で初期化するコンストラクタ」と同じであることに注意しよう。
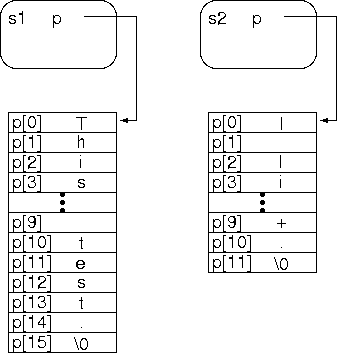
下図に対して代入演算「s2 = s1;」を行ったときに何が起こるかを operator= の定義を見ながら考えてみよ。
「『delete[] p;』が何を消去することに相当するか」などをきちんと考えること。
int main(){
samp x; // (1)
samp y=x; // (2)
samp z;
z = x; // (3)
// 以下、なんらかの処理
}
|
#include <iostream> // cout を使うため
#include <cstring> // strlen 関数、strcpy 関数を使うため
#include <cstdlib> // exit を使うため
using namespace std;
class strtype { // クラス宣言
char *p;
public:
strtype(){ p=0; cout << "デフォルトコンストラクタ\n";} // デフォルトコンストラクタ
strtype(char *s); // 文字列で初期化するためのコンストラクタ
strtype(const strtype &o); // コピーコンストラクタ
~strtype(){delete[] p; cout << "デストラクタ\n";} // デストラクタ
strtype &operator=(const strtype &o); // 代入演算子
char *get(){ return p; }
};
// 文字列で初期化するコンストラクタ
strtype::strtype(char *s){
cout << "文字列で初期化するコンストラクタ\n";
int l;
l = strlen(s)+1; // s の文字列の長さにヌル文字用の1を加える
p = new char[l];
if(!p) {
cout << "メモリ割り当てエラー\n";
exit(1);
}
strcpy(p,s);
}
// コピーコンストラクタ
strtype::strtype(const strtype &o){
cout << "コピーコンストラクタ\n";
int l;
l = strlen(o.p)+1; // o の文字列の長さにヌル文字用の1を加える
p = new char[l];
if(!p) {
cout << "メモリ割り当てエラー\n";
exit(1);
}
strcpy(p,o.p);
}
// 代入演算子
strtype &strtype::operator=(const strtype &o){
cout << "代入演算子\n";
delete[] p; // まず、現在のポインタの先を解放
int l;
l = strlen(o.p)+1; // o の文字列の長さにヌル文字用の1を加える
p = new char[l];
if(!p) {
cout << "メモリ割り当てエラー\n";
exit(1);
}
strcpy(p,o.p);
return(*this); // ここは決まり文句。これにより s1=s2=s3; などといった記述が可能になる。
}
// これは C 言語的な大域的関数
void show(strtype x)
{
char *s;
s = x.get();
cout << s << "\n";
}
int main(){ // main 関数
strtype a("Hello");
strtype b("There");
show(a);
show(b);
// strtype s1("This is a test."); // こちらも有効にして動作を確認してみよ
// strtype s2 = s1;
// strtype s3;
// s3 = s1;
return 0;
}
|
