p = (char *)malloc(SIZE); |
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib> // for malloc/free
using namespace std;
#define SIZE 255
int main(){
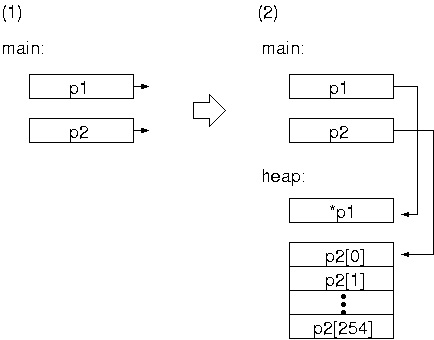
int *p1;
int *p2;
p1 = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int)); // int 型変数1個のメモリ確保
p2 = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int)*SIZE); // int 型の配列 (要素数) のメモリ確保
*p1 = 1000;
cout << "p1 が指している整数型は: " << *p1 << "\n";
// p2 の利用部は各自で例を考えて書いてみること
free(p1); // メモリの解放
free(p2);
return 0;
}
|

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define SIZE 255
int main(){
int *p1;
int *p2;
p1 = new int; // (※) int 型変数1個のメモリ確保
p2 = new int[SIZE]; // (※) int 型の配列 (要素数 SIZE) のメモリ確保
*p1 = 1000;
cout << "p1 が指している整数型は: " << *p1 << "\n";
// p2 の利用部は各自で例を考えて書いてみること
delete p1; // (※) メモリの解放
delete[] p2; // (※) メモリの解放 (1要素と配列とで異なる!!)
return 0;
}
|
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class samp{
int i, j;
public:
samp(){ // デフォルトコンストラクタ
cout << "default constructor\n";
}
samp(int a, int b){ // 引数つきコンストラクタ
i = a;
j = b;
cout << "constructor with arguments\n";
}
~samp(){ cout << "destructor\n";} // デストラクタ
void set_ij(int a, int b){ i=a; j=b;}
int get_product(){ return i*j; }
};
int main(){
samp *p1;
samp *p2;
samp *p3;
p1 = new samp; // オブジェクト1個 (引数なし)
p2 = new samp(6,5); // オブジェクト1個 (引数あり)
p3 = new samp[10]; // オブジェクト10個の配列 (引数なし)
p1->set_ij(4,5);
for(int i=0 ; i<10 ; i++){
p3[i].set_ij(i,i);
}
cout << "p1 の積は: " << p1->get_product() << "\n";
cout << "p2 の積は: " << p2->get_product() << "\n";
for(int i=0 ; i<10 ; i++)
cout << "p3[" << i << "]の積は: " << p3[i].get_product() << "\n";
delete p1;
delete p2;
delete[] p3;
return 0;
}
|
samp **p; // ポインタへのポインタ
p = new samp*[10] // samp 型のポインタの配列 10 個を確保
p[0] = new samp(0,0);
p[1] = new samp(1,1);
…
// 使用する際は p[i]->get_product() のようにアクセス
for(int i=0 ; i<10 ; i++){ // 各ポインタの指すオブジェクトを削除した後…
delete p[i];
}
delete[] p; // ポインタへのポインタを削除
|